Hormone therapy for menopause has emerged as a topic of immense significance, inviting us to delve into the intricacies of managing menopausal symptoms and navigating the complexities of treatment options. This exploration will shed light on the potential benefits and risks associated with hormone therapy, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
As we embark on this journey, we will examine the different types of hormone therapy available, their routes of administration, and the duration of treatment. We will also explore alternative therapies that may provide relief from menopausal symptoms. By providing comprehensive information and fostering a dialogue, we aim to empower individuals to take charge of their health and make choices that align with their unique needs.
Definition and Overview of Hormone Therapy for Menopause

Hormone therapy (HT) is a medical treatment that uses hormones to relieve the symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. HT can also help prevent osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and makes them more likely to break.
There are three main types of HT:
- Estrogen-only therapyis used to treat women who have had a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
- Progestin-only therapyis used to treat women who still have their uterus.
- Combination therapyincludes both estrogen and progestin.
HT has been used for over 50 years to treat the symptoms of menopause. In the past, HT was often prescribed for long periods of time. However, research has shown that long-term use of HT can increase the risk of certain health problems, such as blood clots, heart disease, and breast cancer.
Benefits and Risks of Hormone Therapy
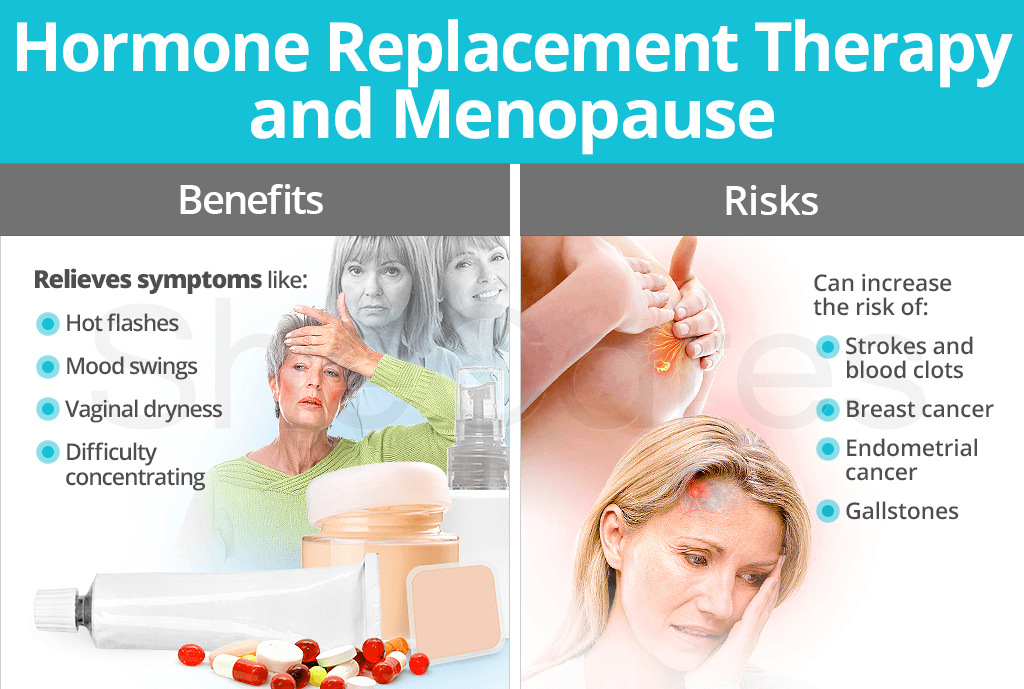
Hormone therapy (HT) is a treatment option for menopausal symptoms. It involves taking hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to replace the hormones that the body stops producing during menopause.
HT can provide several benefits, including relief from hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. It can also help to prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
However, HT also carries some potential risks. These include an increased risk of certain cancers, such as breast cancer and endometrial cancer, as well as an increased risk of blood clots.
The decision of whether or not to take HT is a personal one that should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. The risks and benefits of HT should be carefully weighed for each individual patient.
Benefits of Hormone Therapy
- Relief from hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings
- Prevention of bone loss
- Reduced risk of certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes
Risks of Hormone Therapy
- Increased risk of certain cancers, such as breast cancer and endometrial cancer
- Increased risk of blood clots
Duration and Monitoring of Hormone Therapy: Hormone Therapy For Menopause
The duration of hormone therapy (HT) for menopause is individualized and depends on various factors, including the woman’s age, symptoms, and overall health.
Generally, HT is recommended for the shortest duration possible to relieve menopausal symptoms, typically for 5 years or less. However, some women may benefit from longer-term HT, especially if they have severe symptoms or an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Monitoring of Hormone Therapy
Regular monitoring during HT is essential to assess its effectiveness and manage potential risks.
Monitoring typically involves:
- Physical exams:To check for any changes in blood pressure, weight, and breast health.
- Blood tests:To monitor hormone levels, cholesterol, and liver function.
- Mammograms:To screen for breast cancer, especially in women who are at increased risk.
Alternative Therapies for Menopause
Hormone therapy (HT) is not the only option for managing menopause symptoms. Several alternative therapies can effectively alleviate these symptoms, offering a more natural and holistic approach.
Alternative therapies encompass a wide range of approaches, including lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, and acupuncture. Each therapy has its own unique benefits and risks, and the effectiveness varies among individuals.
Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve menopause symptoms. These include:
- Regular exercise:Physical activity helps reduce hot flashes, improves mood, and promotes better sleep.
- Healthy diet:A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall well-being and may reduce the severity of symptoms.
- Stress management techniques:Yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, which can exacerbate menopause symptoms.
- Sleep hygiene:Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed can improve sleep quality.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs have been traditionally used to alleviate menopause symptoms. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using herbal remedies, as they can interact with medications or have side effects.
- Black cohosh:This herb is believed to reduce hot flashes and improve sleep.
- Red clover:Rich in isoflavones, red clover may help relieve hot flashes and night sweats.
- Evening primrose oil:This oil is a source of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), which may improve skin elasticity and reduce hot flashes.
Acupuncture, Hormone therapy for menopause
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. This ancient Chinese practice is believed to balance energy flow and promote relaxation.
Studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in reducing hot flashes, improving sleep, and alleviating anxiety during menopause.
Patient Education and Decision-Making
Empowering patients with comprehensive knowledge and informed decision-making is crucial in hormone therapy for menopause. Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in providing accurate information, addressing concerns, and guiding patients through the process.
Healthcare Professional’s Role
- Provide detailed information about hormone therapy, including its benefits, risks, and potential side effects.
- Discuss individual patient factors, such as medical history, lifestyle, and personal preferences, to determine the most suitable treatment options.
- Address any misconceptions or concerns patients may have, ensuring they have a clear understanding of the therapy.
- Support patients in making informed choices that align with their values and health goals.
Patient’s Role
- Gather information from reputable sources, including healthcare professionals, reliable websites, and support groups.
- Actively participate in discussions with healthcare providers, asking questions and seeking clarification to fully understand the treatment options.
- Consider personal preferences, lifestyle, and health history when making decisions about hormone therapy.
- Be open to discussing any concerns or side effects experienced during treatment, enabling healthcare professionals to make necessary adjustments.
FAQ Explained
What are the most common symptoms of menopause?
Hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances are among the most common symptoms of menopause.
What are the different types of hormone therapy available for menopause?
Estrogen-only therapy, progestin-only therapy, and combination therapy are the three main types of hormone therapy used to treat menopausal symptoms.
What are the potential benefits of hormone therapy for menopause?
Hormone therapy can alleviate hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and other menopausal symptoms, improving overall quality of life.
What are the potential risks of hormone therapy for menopause?
Hormone therapy may increase the risk of certain cancers, such as breast cancer and endometrial cancer, as well as blood clots.
What are some alternative therapies for menopause?
Lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, and acupuncture are among the alternative therapies that may provide relief from menopausal symptoms.