Having hot flashes is a common experience for many individuals, particularly during hormonal changes like menopause. These sudden feelings of intense heat can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and management strategies can help individuals navigate this phase with greater ease and well-being.
This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of hot flashes, exploring the underlying hormonal triggers, associated physical and emotional symptoms, and effective medical and natural remedies. By providing practical coping mechanisms and highlighting the importance of emotional support, this resource aims to empower individuals to manage hot flashes effectively, improving their overall quality of life.
Causes of Hot Flashes

Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, the transition period when a woman’s menstrual cycle ends. They are caused by a sudden drop in estrogen levels, which triggers a series of physiological changes in the body.
Estrogen is a hormone that helps regulate body temperature. When estrogen levels decline, the body’s thermostat becomes more sensitive to small changes in temperature. This can cause the body to overreact to even slight increases in temperature, resulting in a hot flash.
Age, Weight, and Genetics
The severity of hot flashes can vary depending on a number of factors, including age, weight, and genetics. Older women tend to experience more severe hot flashes than younger women. This is because estrogen levels decline more rapidly with age.
Overweight and obese women are also more likely to experience hot flashes. This is because fat cells produce estrogen, so women with more body fat have higher estrogen levels. When estrogen levels decline, overweight and obese women experience a greater drop in estrogen, which can lead to more severe hot flashes.
Genetics also play a role in the severity of hot flashes. Some women are simply more likely to experience hot flashes than others, regardless of their age or weight.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to hot flashes. These include:
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Caffeine intake
- Spicy foods
- Stress
If you are experiencing hot flashes, it is important to talk to your doctor. There are a number of treatments available to help reduce the severity of hot flashes.
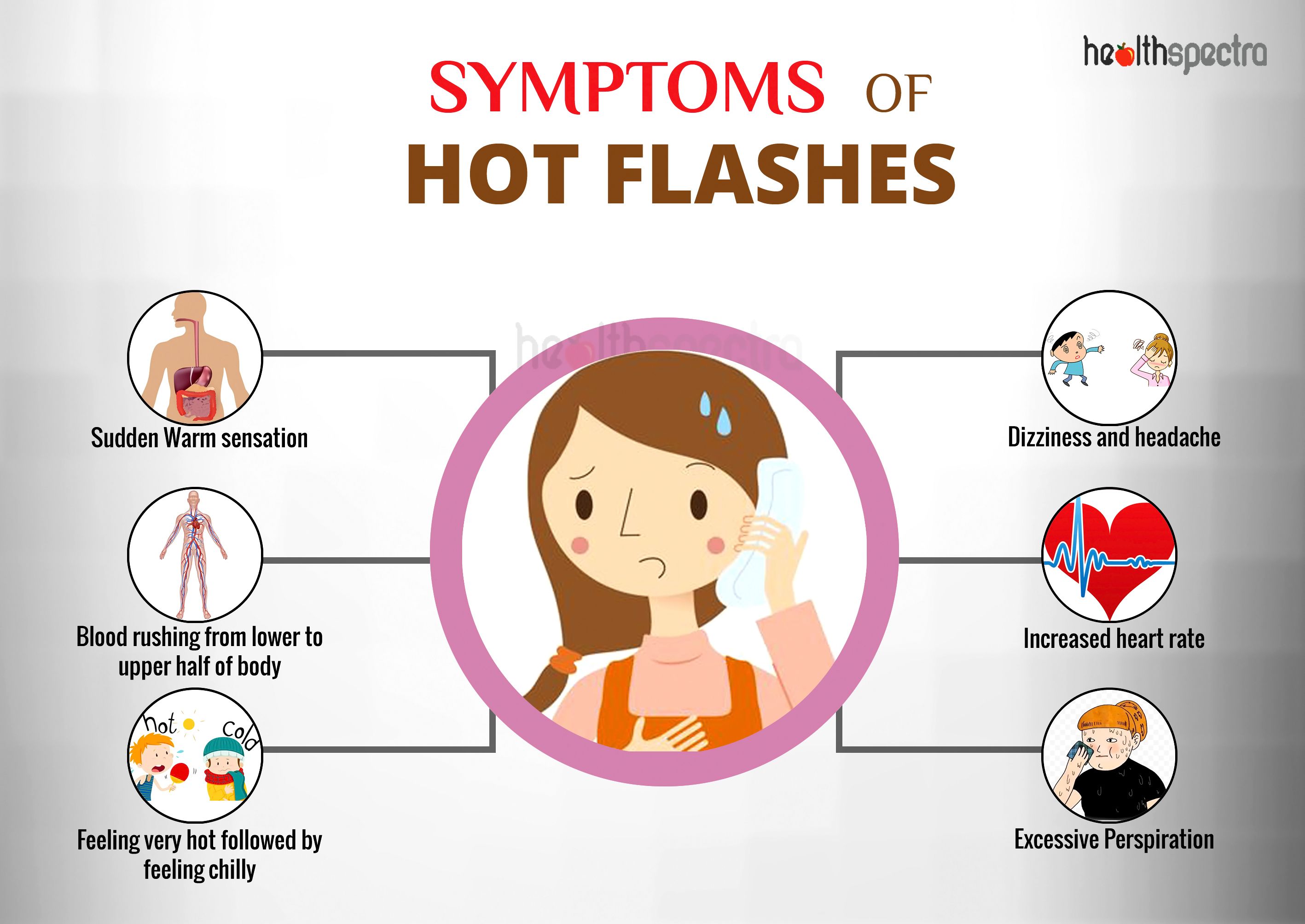
Symptoms and Effects of Hot Flashes: Having Hot Flashes

Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, characterized by sudden and intense feelings of heat that spread over the body, often accompanied by sweating, flushing, and a rapid heartbeat. These episodes can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes and can occur multiple times throughout the day or night.
Physical Symptoms
- Sudden onset of intense heat over the face, neck, and chest
- Sweating and flushing of the skin
- Rapid heartbeat and palpitations
- Chills or goosebumps following the hot flash
Emotional Symptoms
- Irritability and mood swings
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances
Impact on Sleep, Mood, and Quality of Life
Hot flashes can significantly impact sleep quality, as they often disrupt sleep patterns and cause night sweats. This sleep deprivation can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Furthermore, hot flashes can trigger emotional symptoms such as anxiety, mood swings, and irritability, which can affect relationships and overall well-being.
The prevalence of hot flashes among menopausal women varies widely, with estimates ranging from 50% to 80%. The duration of hot flashes can also vary, with some women experiencing them for a few months or years, while others may have them for several years.
Medical Treatments for Hot Flashes
Hot flashes can be managed through various medical treatments. Hormone replacement therapy, antidepressants, and herbal supplements are common options. However, each treatment has its own benefits, side effects, and contraindications.
Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, can also play a role in reducing the severity and frequency of hot flashes.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Replaces hormones that decline during menopause, such as estrogen and progesterone.
- Effective in reducing hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms.
- May increase the risk of certain cancers, blood clots, and heart disease.
- Contraindicated for women with a history of these conditions or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Antidepressants
- Certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), have been shown to reduce hot flashes.
- May also improve mood and sleep.
- Potential side effects include nausea, headache, and sexual dysfunction.
- Contraindicated for people with certain medical conditions, such as uncontrolled epilepsy or glaucoma.
Herbal Supplements
- Some herbal supplements, such as black cohosh and red clover, have been traditionally used to relieve hot flashes.
- Limited scientific evidence supports their effectiveness.
- Potential side effects and interactions with other medications should be considered.
- Contraindicated for people with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease.
Natural Remedies for Hot Flashes
Natural remedies can offer relief from hot flashes by addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances or reducing stress levels. However, it’s important to note that individual responses may vary, and it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any new remedies into your routine.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow. It may help regulate hormone levels and reduce stress, thereby alleviating hot flashes. However, it requires multiple sessions and may not be suitable for everyone.
Yoga
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote relaxation and stress reduction. Certain yoga poses, such as the child’s pose and forward folds, may help cool the body and reduce hot flashes. Yoga is generally safe, but it’s recommended to consult with a qualified instructor for proper guidance.
Dietary Changes, Having hot flashes
Dietary changes can play a significant role in managing hot flashes. Certain foods, such as spicy dishes, caffeine, and alcohol, can trigger or worsen hot flashes. Avoiding or limiting these foods may help reduce their frequency and severity.
- Cooling foods:Cucumbers, watermelon, and mint may have cooling effects and provide relief from hot flashes.
- Soy products:Soy contains isoflavones, which are plant-based compounds with estrogen-like effects. They may help regulate hormone levels and reduce hot flashes.
- Flaxseed:Flaxseed is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce the intensity and frequency of hot flashes.
Coping Mechanisms for Hot Flashes
Hot flashes can be disruptive and uncomfortable, but there are several coping mechanisms that can help manage their intensity and frequency.
These strategies include relaxation techniques, cooling strategies, and stress management. Each approach offers unique benefits and can be tailored to individual needs.
Relaxation Techniques
- Deep breathing exercises:Inhale slowly and deeply through the nose, filling the lungs with air. Exhale slowly through the mouth, releasing tension and calming the body.
- Meditation:Focus on the present moment, clearing the mind of distracting thoughts. Meditation promotes relaxation and reduces stress, which can trigger hot flashes.
- Yoga or Tai Chi:These mind-body practices combine gentle movements, breathing exercises, and meditation. They promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
Cooling Strategies
- Cool showers or baths:Immerse yourself in cool water to reduce body temperature and provide instant relief from hot flashes.
- Cold compresses:Apply cold compresses to the neck, forehead, or wrists to cool the body from the inside out.
- Wear loose, breathable clothing:Choose fabrics like cotton or linen that allow the skin to breathe and prevent overheating.
- Use a fan or air conditioner:Circulate cool air to keep the body temperature comfortable.
Stress Management
- Exercise regularly:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting and stress-reducing effects.
- Get enough sleep:Sleep deprivation can exacerbate hot flashes. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Practice relaxation techniques:The relaxation techniques mentioned above can also help manage stress and reduce the frequency of hot flashes.
- Seek professional help:If stress is a significant trigger for hot flashes, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor.
Emotional Support and Self-Care
Coping with hot flashes also involves emotional support and self-care. Sharing experiences with others who understand can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation.
Prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as spending time in nature, reading, or pursuing hobbies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common triggers for hot flashes?
Hot flashes are primarily triggered by hormonal changes, particularly a decline in estrogen levels during menopause. Other potential triggers include certain medications, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors like stress, caffeine, and alcohol consumption.
Can hot flashes be prevented?
While it is not always possible to prevent hot flashes, certain lifestyle modifications can help reduce their frequency and severity. These include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol.
Are hot flashes a sign of a serious medical condition?
In most cases, hot flashes are not indicative of a serious medical condition. However, if hot flashes are accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or excessive sweating, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.