Bleeding during menopause is a common experience for many women, and it can be a source of concern. This guide will provide an overview of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bleeding during menopause.
Menopause is a natural process that occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop producing eggs. This can lead to a number of changes in the body, including changes in hormone levels. These changes can cause the lining of the uterus to become thinner and more fragile, which can lead to bleeding.
Bleeding During Menopause
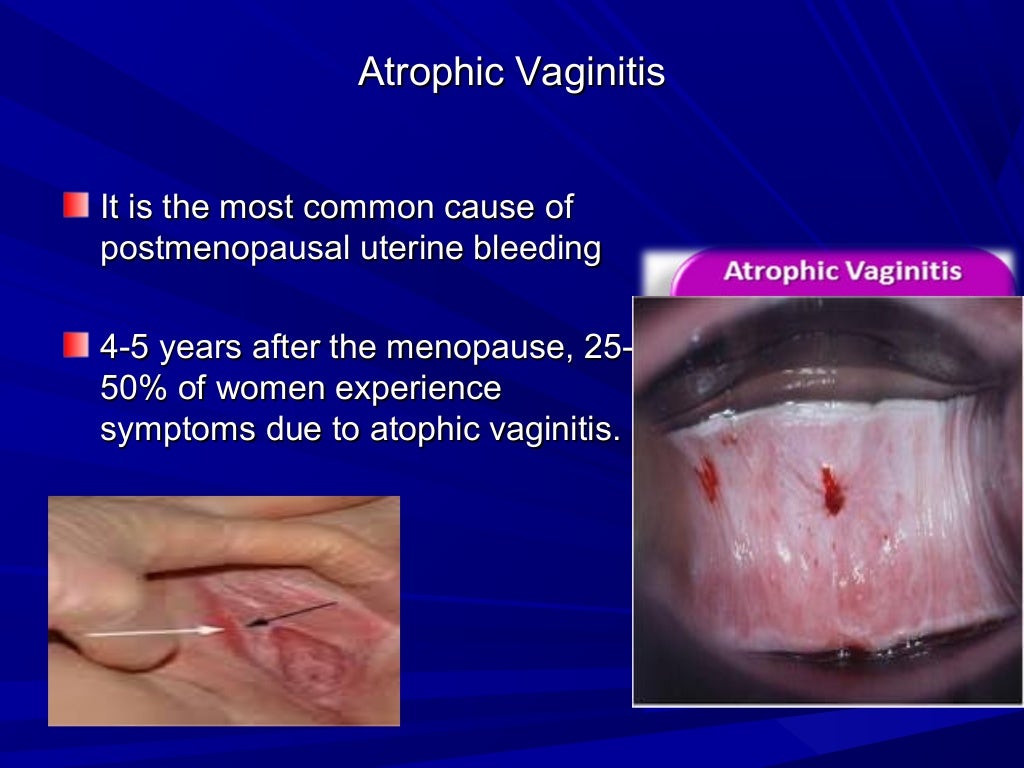
During menopause, the ovaries stop producing the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which can lead to changes in the menstrual cycle and bleeding patterns. Some women experience no bleeding during menopause, while others may have irregular bleeding or spotting. In some cases, bleeding during menopause can be heavy or prolonged.
Causes of Bleeding During Menopause
The most common causes of bleeding during menopause include:
- Hormonal imbalances:The decline in estrogen and progesterone levels during menopause can cause the uterine lining to become thin and irregular, which can lead to bleeding.
- Endometrial hyperplasia:This is a condition in which the uterine lining becomes thick and overgrown. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances or by taking certain medications, such as tamoxifen.
- Uterine fibroids:These are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause bleeding during menopause.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Bleeding during menopause is not a normal occurrence and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Common symptoms associated with bleeding during menopause include:
- Abdominal pain
- Cramping
- Fatigue
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Mood swings
Diagnostic tests that may be used to determine the cause of bleeding during menopause include:
- Pelvic exams
- Transvaginal ultrasounds
- Endometrial biopsies
Timely diagnosis is important to rule out any underlying medical conditions, such as endometrial cancer, uterine fibroids, or cervical polyps.
Treatment Options

Bleeding during menopause can be managed through various treatment options, depending on the severity and underlying cause. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual needs and circumstances.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves administering synthetic hormones, such as estrogen and progestin, to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce bleeding. It can effectively alleviate hot flashes, night sweats, and other menopausal symptoms.
Benefits:
- Reduces bleeding and improves menstrual regularity
- Relieves hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms
- May protect against osteoporosis
Risks:
- Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart disease
- May cause breast tenderness, headaches, and nausea
Endometrial Ablation
Endometrial ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that destroys the lining of the uterus (endometrium), reducing or eliminating bleeding. It is suitable for women who have completed their childbearing.
Benefits:
- Highly effective in stopping bleeding
- Less invasive than hysterectomy
Risks:
- May not be suitable for all women, especially those with certain medical conditions
- Can cause uterine perforation or damage to surrounding organs
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy involves the surgical removal of the uterus. It is the most effective treatment for bleeding during menopause, but it is also the most invasive and has the longest recovery time.
Benefits:
- Permanently stops bleeding
- May relieve other menopausal symptoms, such as pain and pressure
Risks:
- Major surgery with potential complications, including infection, bleeding, and blood clots
- May cause urinary incontinence or other long-term side effects
Management and Prevention

Managing and preventing bleeding during menopause involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Here are some tips and strategies:
Lifestyle Modifications:
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can help regulate hormone levels and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding during menopause. Excess weight can contribute to hormonal imbalances that may lead to irregular bleeding.
Exercising Regularly
Regular exercise helps improve circulation, which can reduce the risk of blood clots and heavy bleeding. Exercise also promotes overall health and well-being, which can help manage stress and other factors that may contribute to bleeding.
Reducing Stress
Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations that may lead to irregular bleeding. Managing stress through techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can help regulate hormones and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
Managing Bleeding
Using Sanitary Pads or Tampons:
Sanitary pads and tampons are effective ways to absorb menstrual blood and manage bleeding during menopause. Choose products that are comfortable and provide adequate absorbency for your flow.
Avoiding Strenuous Activity:
Strenuous activity can increase blood flow and worsen bleeding. Avoid activities that put excessive strain on your body during periods of heavy bleeding.
Getting Enough Rest:
Getting enough rest can help reduce stress and improve overall health, which may positively impact bleeding during menopause. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
Support Groups and Resources, Bleeding during menopause
Connecting with other women experiencing similar symptoms can provide support and encouragement. Support groups and online forums offer a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others.
Additionally, healthcare professionals, such as gynecologists and nurse practitioners, can provide guidance, treatment options, and support during menopause.
FAQ Explained: Bleeding During Menopause
What are the causes of bleeding during menopause?
The most common cause of bleeding during menopause is hormonal imbalances. Other causes include endometrial hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, and cancer.
What are the symptoms of bleeding during menopause?
The symptoms of bleeding during menopause can vary depending on the cause. Common symptoms include spotting, breakthrough bleeding, and heavy bleeding.
How is bleeding during menopause treated?
The treatment for bleeding during menopause will depend on the cause. Treatment options include hormone replacement therapy, endometrial ablation, and hysterectomy.