Menopause symptoms and treatment encompass a wide range of physical, emotional, and lifestyle changes that women experience during this transitionary phase. Understanding these symptoms and available treatments can empower women to navigate this journey with confidence and well-being.
The prevalence and impact of menopause are significant, affecting millions of women worldwide. Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings, anxiety, and depression. These symptoms can disrupt daily life, affecting sleep, relationships, and overall quality of life.
Introduction

Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although it can vary significantly from woman to woman.
Menopause is caused by a decline in the production of estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that are essential for reproduction. This decline can lead to a variety of symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings.
Prevalence and Impact of Menopause, Menopause symptoms and treatment
Menopause is a common experience for women around the world. In the United States, approximately 1.3 million women reach menopause each year. The symptoms of menopause can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life, interfering with her work, relationships, and overall well-being.
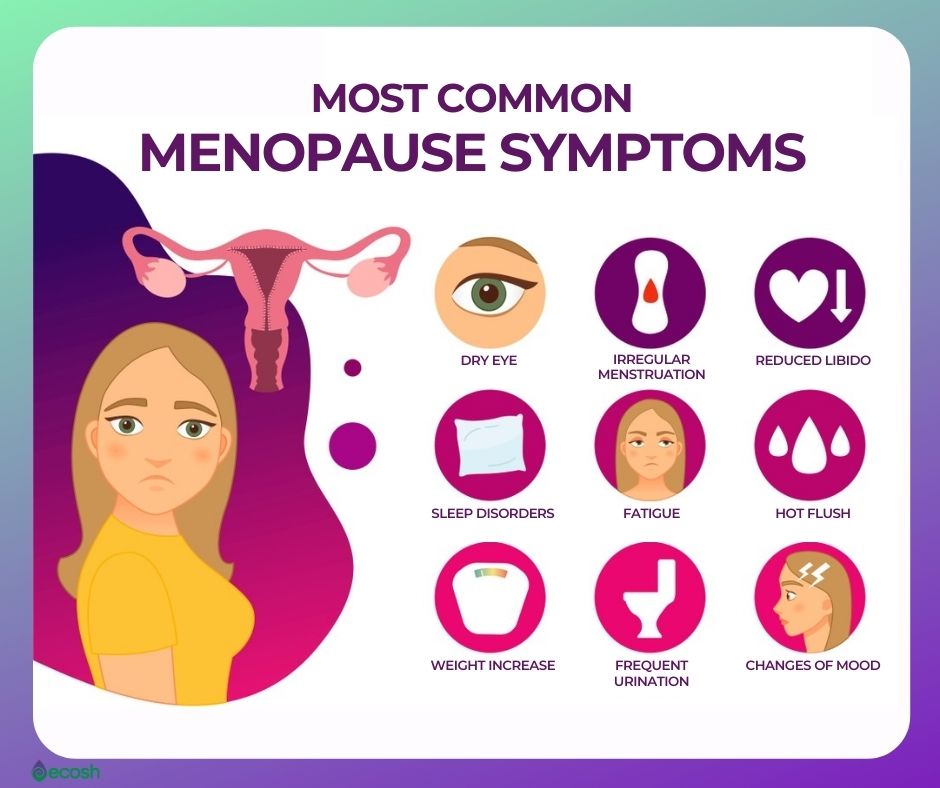
Common Menopause Symptoms
Menopause, a natural transition in a woman’s life, marks the end of her reproductive years. It is characterized by a decline in the production of the hormone estrogen, which leads to a range of physical and emotional symptoms.
Physical Symptoms
The most common physical symptoms of menopause include:
- Hot flashes:Sudden feelings of intense heat and sweating, typically lasting a few minutes.
- Night sweats:Hot flashes that occur during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep and discomfort.
- Vaginal dryness:A decrease in the production of vaginal fluids, causing dryness, itching, and discomfort during intercourse.
- Osteoporosis:A condition characterized by the loss of bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Weight gain:Changes in metabolism and hormone levels can lead to weight gain during menopause.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms
In addition to physical symptoms, menopause can also affect a woman’s emotional and psychological well-being:
- Mood swings:Fluctuations in mood, ranging from irritability to sadness.
- Anxiety:Increased feelings of worry, nervousness, and restlessness.
- Depression:Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
- Cognitive changes:Difficulty concentrating, remembering, and making decisions.
- Sleep disturbances:Difficulty falling or staying asleep, leading to fatigue and irritability.
Medical Treatments for Menopause
Menopause can bring about a range of symptoms that can impact daily life. While lifestyle changes and natural remedies can provide some relief, medical treatments may be necessary for managing more severe symptoms.
Medical treatments for menopause aim to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. These treatments may include hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and other medications.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves the administration of hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to replace the hormones that decline during menopause. HRT can effectively reduce hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms associated with estrogen deficiency.
However, HRT is not without risks. Potential side effects include blood clots, stroke, heart disease, and breast cancer. The risks and benefits of HRT should be carefully considered before starting treatment.
Other Medical Treatments
In addition to HRT, other medications can be used to manage specific menopause symptoms. These include:
- Antidepressants:Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can help improve mood and reduce anxiety, which are common symptoms during menopause.
- Anti-anxiety medications:Benzodiazepines and buspirone can provide relief from anxiety and sleep disturbances.
- Gabapentin:This medication can reduce hot flashes and night sweats.
- Clonidine:This medication can also help reduce hot flashes.
The choice of medical treatment for menopause depends on individual symptoms and risk factors. It is important to discuss the options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach.
Non-Medical Approaches to Menopause Management: Menopause Symptoms And Treatment
Menopause can bring about a range of uncomfortable symptoms, but there are many non-medical strategies that can help manage them. These approaches focus on lifestyle changes and natural remedies to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Managing Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are one of the most common menopause symptoms. To manage them effectively, consider the following tips:
- Dress in layers: This allows you to adjust your clothing as needed to cool down or warm up.
- Use cooling products: Cooling towels, neck wraps, and fans can provide instant relief from hot flashes.
- Avoid triggers: Certain foods, drinks, and activities can trigger hot flashes. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce their frequency.
Improving Sleep Quality
Sleep disturbances are another common issue during menopause. To improve sleep quality:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends, can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: This could include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed: These substances can interfere with sleep.
Exercise and Diet
Exercise and diet play a crucial role in managing menopause symptoms.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help reduce hot flashes, improve sleep quality, and boost overall mood.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients that support overall well-being during menopause.
- Consider soy products: Soy contains isoflavones, which are plant compounds that have estrogen-like effects and may help alleviate some menopause symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes and Menopause
Menopause can significantly impact a woman’s overall well-being, and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in managing its symptoms. Understanding how certain habits, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and caffeine intake, can affect menopause symptoms is essential. Additionally, regular exercise, a healthy diet, and effective stress management techniques can greatly contribute to alleviating these symptoms and improving overall health during this transition.
Smoking and Menopause
Smoking is strongly associated with earlier menopause onset and more severe menopausal symptoms. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the ovaries, which can lead to premature ovarian failure. Additionally, smoking damages DNA and accelerates the aging process, contributing to the earlier onset of menopause.
Alcohol Consumption and Menopause
Excessive alcohol consumption can worsen hot flashes and night sweats, two common menopause symptoms. Alcohol can interfere with the body’s temperature regulation, causing sudden fluctuations and increased sweating. Additionally, alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and irritability.
Caffeine Intake and Menopause
Caffeine is a stimulant that can trigger hot flashes and night sweats in some women. It can also increase anxiety and sleep disturbances, which are common during menopause. Therefore, limiting caffeine intake may help reduce the severity of these symptoms.
Importance of Regular Exercise and a Healthy Diet
Regular exercise is crucial for overall health and well-being during menopause. It helps reduce body fat, which can contribute to hot flashes, and improves mood by releasing endorphins. Exercise also strengthens bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, a common concern during menopause.A
healthy diet is equally important. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients that support overall health and may help reduce menopausal symptoms. Calcium-rich foods are particularly important for maintaining bone health during this time.
Managing Stress During Menopause
Stress can exacerbate menopausal symptoms, so finding effective stress management techniques is crucial. Regular exercise, yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. Seeking support from family, friends, or a therapist can also provide emotional support and coping mechanisms.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Menopause

Menopause can bring about a range of emotional and psychological challenges for women. These can include feelings of loss and grief, as well as anxiety, depression, and irritability. Understanding these challenges and developing coping mechanisms can help women navigate this transition more effectively.
Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms for managing the emotional and psychological challenges of menopause can include:
- Joining support groups or connecting with other women going through similar experiences.
- Seeking professional therapy or counseling to process feelings and develop strategies for managing symptoms.
- Engaging in relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep.
- Exploring complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or massage therapy.
Long-Term Health Implications of Menopause
Menopause can have long-term health implications, including an increased risk of osteoporosis and heart disease. Understanding these risks and taking preventive measures is crucial for maintaining health and well-being during and after menopause.
After menopause, the decline in estrogen levels leads to a decrease in bone density, making women more susceptible to osteoporosis. This condition weakens bones, increasing the risk of fractures and breaks, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist.
Preventive Measures for Osteoporosis
- Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements:Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet or supplements to support bone health.
- Regular Exercise:Engage in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, or dancing, to promote bone strength.
- Fall Prevention:Implement measures to reduce the risk of falls, such as improving home safety and maintaining good balance.
- Smoking Cessation:Smoking damages bones and increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Bone Density Screening:Undergo regular bone density screenings to monitor bone health and assess the need for treatment.
Menopause also increases the risk of heart disease. The decline in estrogen levels can lead to changes in cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and blood clotting, all of which can contribute to heart disease.
Preventive Measures for Heart Disease
- Healthy Diet:Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Exercise:Engage in regular aerobic exercise to improve cardiovascular health.
- Smoking Cessation:Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
- Blood Pressure Control:Monitor blood pressure and take medication as prescribed to keep it under control.
- Cholesterol Management:Maintain healthy cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary.
- Mammograms:Regular mammograms are essential for early detection of breast cancer, which is more common after menopause.
Conclusion
Menopause is a natural transition in a woman’s life, marked by the cessation of menstrual periods and significant hormonal changes. Understanding the symptoms, treatments, and potential health implications is crucial for women to navigate this phase effectively.
Women experiencing menopausal symptoms are strongly encouraged to seek medical advice. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance, recommend appropriate treatments, and address any underlying health concerns. By embracing a proactive approach to menopause management, women can minimize discomfort, maintain overall well-being, and ensure a healthy and fulfilling life during and beyond this transition.
FAQ Corner
What are the most common physical symptoms of menopause?
Hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances are among the most prevalent physical symptoms.
How can I manage hot flashes effectively?
Dressing in layers, using cooling products, and avoiding triggers such as caffeine and alcohol can help alleviate hot flashes.
Is hormone replacement therapy (HRT) the only treatment option for menopause symptoms?
No, there are various non-medical approaches and alternative medical treatments available, including antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and lifestyle modifications.
What are the long-term health implications of menopause?
Menopause increases the risk of osteoporosis and heart disease, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures such as calcium and vitamin D supplements, regular exercise, and a healthy diet.
How can I cope with the emotional challenges of menopause?
Support groups, therapy, and open communication with loved ones can provide emotional support and coping mechanisms for managing the emotional challenges associated with menopause.